Data analysis plays an increasingly important role in learning, working, and researching. How to present complex data in a simple and clear way is a challenge faced by everyone. As one of the most commonly used presentation tools, PowerPoint can effectively convey the results of data analysis to the audience through proper design and content presentation.
Basic structure of data analysis PowerPoint presentation
To make a data analysis presentation, you first need to have a clear structure. This helps the audience understand your analysis process and conclusions, and also makes it easier for you to present the content in an organized manner. Generally speaking, a data analysis PowerPoint presentation usually contains the following parts:
First is the cover page, which needs to be concise and attractive, usually including the topic of the presentation, the date, and the speaker's information. The design of the cover page is the first impression given to the audience, so make sure it is visually concise and clear, avoiding too much text and messy elements.
Next is the objectives and agenda section. In this section, you need to clarify the purpose of the presentation and briefly list the content or steps to be presented. This not only helps the audience understand what you are going to explain, but also allows them to have a general expectation of the entire presentation.
The data background section is a brief introduction to the source and background of the data. This part is especially important for audiences who do not know the data source in detail. It can help them understand the background of the data and enhance the credibility of the presentation.
Then comes the introduction of the analysis method. In this part, you need to explain the data analysis tools or methods you use, such as regression analysis, trend analysis, prediction models, etc. These contents help the audience understand how you draw conclusions and increase the professionalism of the presentation.
The most important part is the presentation of results, which is usually presented intuitively in the form of charts, images, tables, etc. The data chart is the part that attracts the most attention from the audience. Through charts and images, complex digital data is transformed into intuitive visual effects, which can better help the audience understand the meaning behind the data.
Finally, there is the conclusion and suggestion part. At the end of the presentation, you need to summarize the main findings of the analysis and make corresponding suggestions or action plans based on the data analysis. The conclusion should be concise and clear, avoiding too much technical language, so that the audience can understand and absorb it easily.
How to choose the right data presentation format
When making a data analysis PowerPoint presentation, it is crucial to choose the right data presentation format. Different types of data are suitable for presentation in different ways, which can make the data clearer and easier to understand.
Bar charts and line charts are commonly used tools for showing data trends and comparisons. Bar charts are suitable for showing comparisons between different categories, while line charts are suitable for showing data trends that change over time. Pie charts are suitable for showing percentage data, especially when analyzing market share or components. For more complex time series data, trend charts and heat maps can help viewers quickly capture changing trends and anomalies.
For data involving multiple variables, dashboards can integrate multiple indicators on one interface to provide a comprehensive view at a glance. Especially when showing corporate operating data, dashboards can effectively summarize multi-dimensional data and help viewers quickly understand the overall situation.
Use data visualization tools to optimize presentation effects
In addition to manually making charts in PowerPoint, using data visualization tools to improve presentation effects is also a very effective strategy. Some professional data visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, etc. can process and display more complex data sets, and provide rich chart styles and interactive functions to help users create more dynamic and professional presentations.
For example, Power BI and Tableau can easily transform large-scale data sets into visual charts, and can interactively display data in real-time presentations to enhance audience participation and understanding. If you need to use a simpler tool, Smallppt is also a good choice. It provides users with a large number of data visualization templates, helping non-design professionals to easily create beautiful charts and presentations.
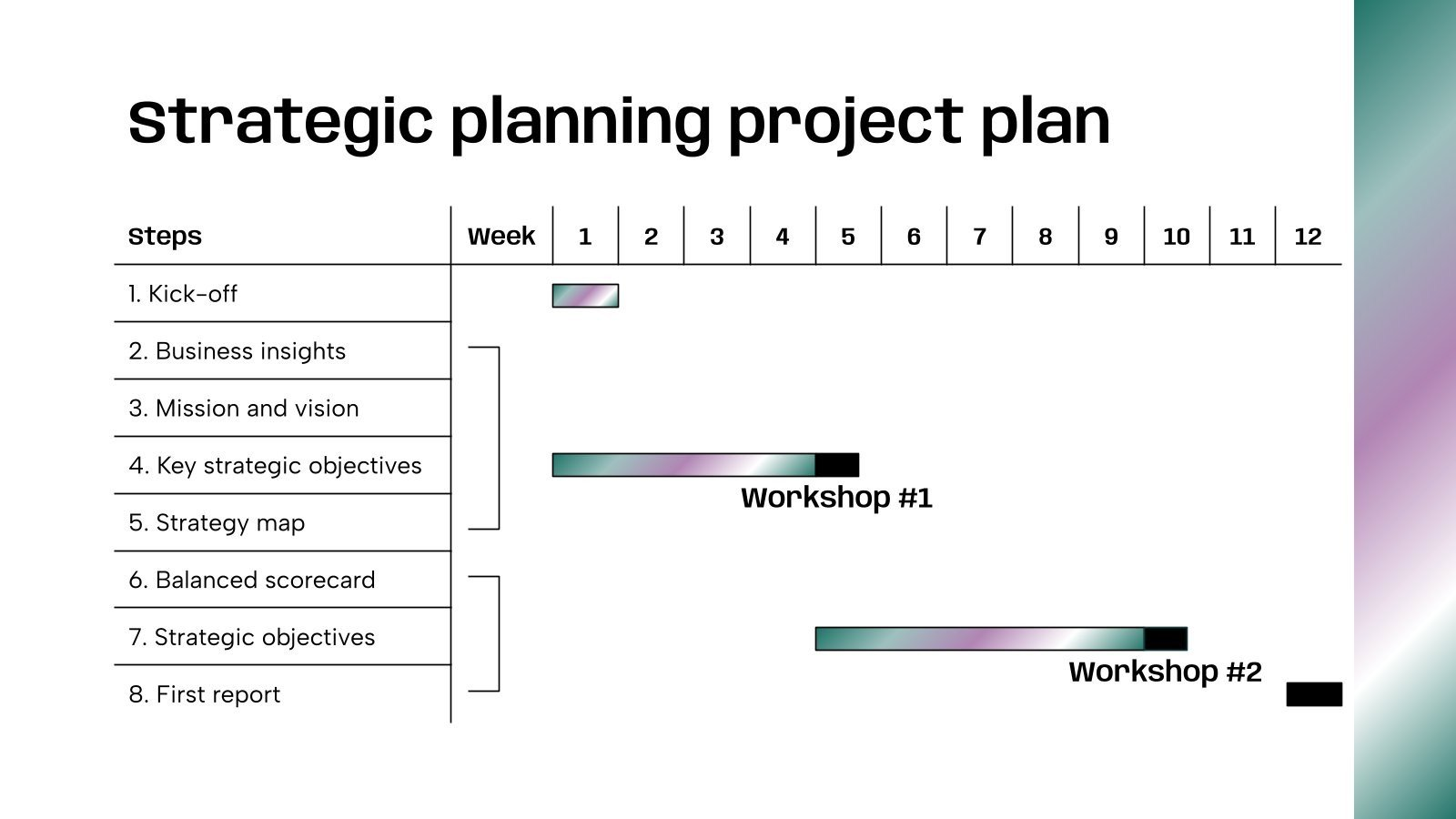
Design Tips: How to Make Data Analysis Presentations More Attractive
The design of data analysis presentations is not only about beauty, but also about the communication effect of information. Good design can help the audience better understand the content and avoid information overload.
First of all, concise and clear design is the key. Avoid placing too many text or charts on one slide, and focus on showing the most important data. Each slide only conveys one clear message so that the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Consistent design is also not to be ignored. The uniformity of fonts, colors, and layout will make your presentation look more professional. Make sure the style of each slide is consistent and avoid using too many different colors and fonts.
High-contrast design can also enhance readability. Make sure there is enough contrast between the text and the background, and avoid using illegible light backgrounds or overly similar color combinations, which will help the audience read the information on the slide more easily.
Finally, moderate use of animation effects can help highlight key points, but avoid overuse. Too much animation may distract the audience from the content. Animation should be simple, smooth, and used to emphasize key data or transition effects.
Common mistakes in data analysis presentations and how to avoid them
When making a data analysis presentation, it is crucial to avoid common mistakes. One common mistake is overly complex charts. Complex charts can easily make the audience lose themselves in the data, and it is best to ensure that each chart is clear, concise, and easy to interpret.
Another common problem is the lack of clear conclusions. The core of data analysis is to draw conclusions, so at the end of the presentation, it is important to clearly summarize the results of the analysis and provide practical recommendations. Without a clear conclusion, the audience may be confused and unsure of what to do next.
In addition, ignoring the target audience is also a common mistake. It is important to adjust the complexity and presentation of the content according to the background and needs of the audience. For non-professional audiences, avoid using too many technical terms and try to express them in simple language.
Conclusion
Making a good data analysis PowerPoint presentation is not just about displaying data on slides, but also about conveying complex analysis results to the audience through reasonable design and clear structure. By choosing the right data presentation format, using data visualization tools, paying attention to design details and avoiding common mistakes, you can create a presentation that is both beautiful and professional, helping the audience to accurately understand your analysis.
Whether it is a business report, academic research, or data presentation in other occasions, mastering how to create an effective data analysis PowerPoint presentation is a vital skill. I hope that with the guidance of this article, you can easily create your own data analysis presentation and leave a deep impression on the audience.